Humanitarian and development monitoring involves tracking and assessing the progress and impact of interventions aimed at improving the lives of individuals and communities.
Here are some key steps in the monitoring and evaluation process:
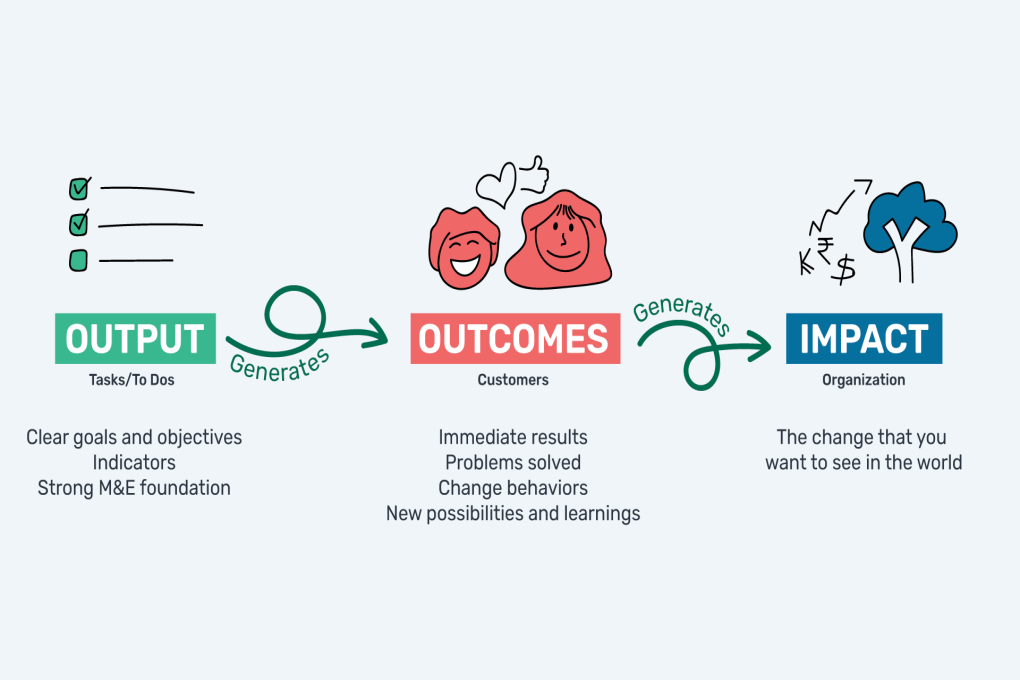
Define objectives and indicators: The first step in monitoring is to define clear objectives for the intervention and develop indicators that will be used to measure progress and impact.
Collect data: Once objectives and indicators are defined, data must be collected to track progress. This may involve conducting surveys, interviews, or focus groups with program beneficiaries and stakeholders, as well as gathering data on program activities and outputs.
Analyze data: After data is collected, it must be analyzed to identify trends, patterns, and areas of success or challenge. This may involve using statistical methods to analyze quantitative data and conducting a qualitative analysis of open-ended responses.
Report findings: Once data is analyzed, findings must be reported to stakeholders, including program managers, donors, and program beneficiaries. This may involve creating reports, presentations, and visualizations to communicate the results of the monitoring process.
Use findings for program improvement: Finally, findings from the monitoring process should be used to improve the program. This may involve making changes to program design or implementation, modifying program objectives, or reallocating resources to areas of greater need.
Overall, monitoring is a critical component of humanitarian and development work. By tracking progress and impact, organizations can ensure that interventions are effective, efficient, and making a positive impact on the lives of the communities they serve.












